About Me
About Me
DEFINITIONS
-
Music production: Music production is the process of creating a recorded music project. It includes all the recording sessions, organizing and programming the recording resources and the budget, and supervision of the recording session, the mix and the master session.
-
daw: Digital Audio Workstation, digital program to manipulate audio files.
-
mix: Process during the recording session and after it for balancing the relative volume and the equalizing of the sound sources that compose the piece you’re working on. In this phase effects such as Compression, Panning, Limitation or Modulators are used to regulate the dinamics of the sound, the panning or the sound formant.
-
master: It’s the last step of the audio postproduction process. Its purpose is to balance the sound elements of a stereo mix and optimize the reproduction in every sistem or format.
-
plug-in: Computerized app that interacts with another one to add a function or additional utility. In Music Production they’re known as VSTs
XPand 2
Electronic/Organic sounds bank
autotune
Modulation and tunning voice tool (Automatic)
melodyne
Modulation and tunning voice tool (Manual)
Kickstar
Volume automatizer at “four on the floor” to crear a Sidechain effect
Compress bear
Dynamic parallel compressor
sausage fattener
Mix of compressors, saturators and limiters used to “fatten” the sound.
cubase maximizer
Advanced mastering VST
ozone izotope
Widener stereo sound image VST
mloudness analizer
Signal Analizer that indicates the dynamic range, peaks and frequencies. It’s used to adap the final audio to the requirements of the diferent audio platforms (Youtube, Soundcloud, Spotify…)
-
fx: Electronic devices that affect the sound of a electronic instrument or any source of sound.
-
compressor: Electronic sound processor destined to reducing the dynamic range of the signal. This is acomplished reducing the gain of the signal when it gets over the volume limit (dBs), called threshold .
-






-
- Gain: Magnitude that expresses the relation between the amplitude of an output signal and the input signal.
- Gain: Magnitude that expresses the relation between the amplitude of an output signal and the input signal
-
dynamic range:: The margin that’s between the peak level and the noise level in the back, measured in decibels (dB).
-
Limiter: Tool that limits the signal output to the desired quantity, reducing the peaks and the dynamic range. It’s similar to a compressor, but while a compressor reduces the signal gradually, a limiter cuts it all over.
- Gain: Magnitude that expresses the relation between the amplitude of an output signal and the input signal.
-
-
equalizer: Tool that modifies the volume of the content of the frequencies of the signal that’s being processed.
-
frequency spectrum: Graphic representation of the sound amplitude, which a human is capable of perceiving (20Hz-20000Hz)
-
-
reverb: Also known as echo, its an effect that gives amplitude and dimension to a sound.
-
theory: Reverb comes from the word “reverberation, which refers to a sound phenomenon that’s produced in enclosures or closed halls in which a sound affects over the different surfaces reflecting itself a big quantity of times, provoking the reflections to augment in quantity and density, The auditory system isn’t capable of differentiate the individual reflections and processes them as a whole piece of sound. It is similar to a video and its division by frames.
-
-
delay: Sound effect which consists in the multiplication and delaying of a sound signal.
-
mono delay: Effect that places the repetitions of the signal in the monografic frequencies band.
-
stereo delay: Effect that places the repetitions of the signal in the stereo frequencies band, with a slight time delay between each L and R channel.
-
ping pong delay: Effect that places the repetitions of the signal in the stereo frequencies band., and alternates with Panning between the Left and Right channel (L and R).
-
-
distorsion: Effect based on the alteration of the sound waves reciebed from an amplified instrument and transformed into a more saturated signal. The sound that creates it’s given by the amount of harmonics and inharmonics that are being added, resulting into a dirty and less accurate sound.
-
saturation: Term used to design the sound in which the distortion of the signal extremes to the point where the sound gets saturated of distortion.
-
bitcrusher: Distortion produced by the reduction of the resolution/number of bits that contain an audio piece.
-
-
techniques
-
sidechain: Use of compression taking the input signal volume to determine how aggressively it reduces gain in its output signal.
-
multiband compression: Use of compression in a range of frequencies in order to reduce gain and control the dynamics of a signal.
-
sampling: Taking a piece or sample of a previous recorded sound to reuse it as a instrument or a different audio recording.
-
-
sample: Piece of audio used from a song onto another one.
-
royalties: Payments that belong to the copyright holder of a product in exchange of its exploitation.
-
distributor: Company that has the achievement of distributing a product, in order to make a big amount of sales out of it.
-
midi: Musical Instrument Digital Interface. It allows the exchange of information between several connected musical equipment and also between these and a personal computer.
-
mono: A signal recorded with only one microphone. It’s reproduced the same in both L and R channels of a media player system.
-
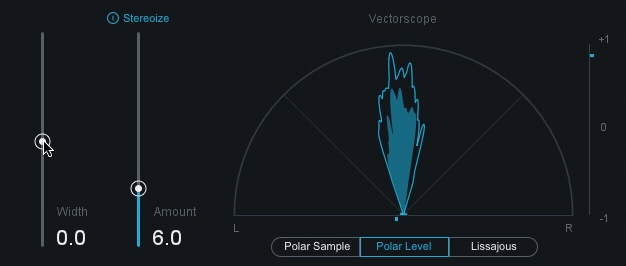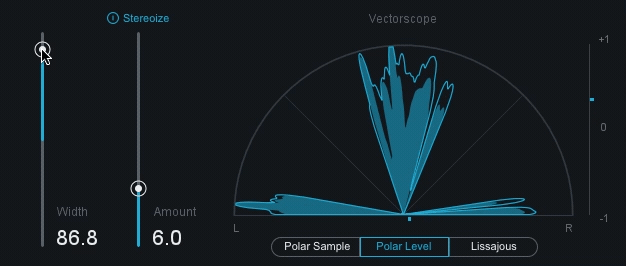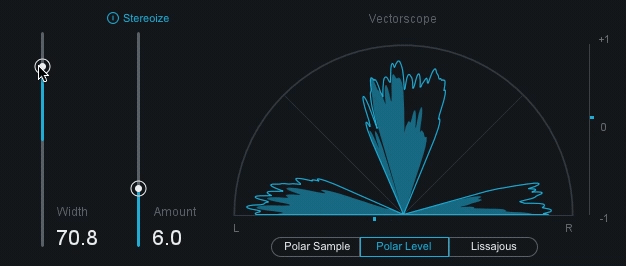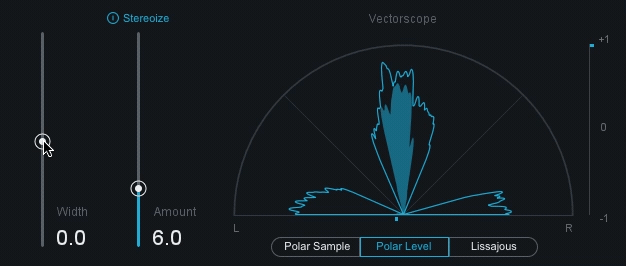
stereo: A signal recorded and reproduced in to different channels.

